FAQ about Agriculture Analytics
1. What is a Multispectral Camera ?
Multispectral cameras are commonly found among Agriculture & Forestry applications of drones. The role of a multispectral sensor is to measure for a plant, the percentage of reflected light at different wavelengths, both in the visible and non-visible parts of the light spectrum that are of interest for vegetation. Typically plants reflect green light and absorb red and blue. But plants also reflect light in non-visible spectrum, in the Near-Infrared (NIR).
This remote sensoring method allows to access to valuable information about plant health, its evolution in relationship to its environment : soil, sunlight, humidity, reaction to agricultural inputs such as fertilizers, among other factors affecting plant life.
1.1. Principle
Light absorption and reflection by plants actually differs according to the light wavelength. Each color in the visible spectrum, for instance, corresponds to a certain wavelength.
1.2. How does a plant reflect light ?
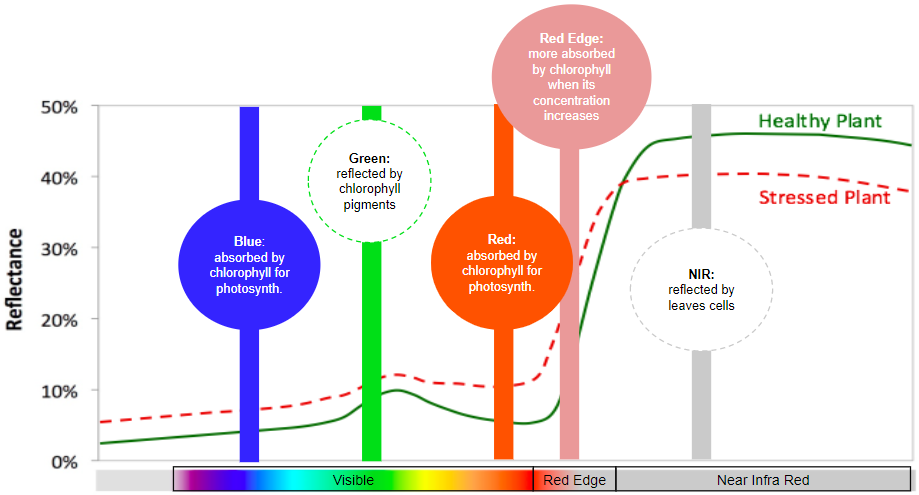
A multipectral camera uses as many single sensors as the numbers of wavelengths to monitor. For instance a Micasense RedEdge is made of 5 sensors each fitted with a specific optical filter to capture light in the targetted wavelength. Combining the inputs of each sensor allows to compute the vegetation indices that are key to evaluate plant and crops condition; collected images pixels values actually account for the percentage of reflectance at the specific wavelength.
The list of Aether currently supported multispectral cameras can be found here.
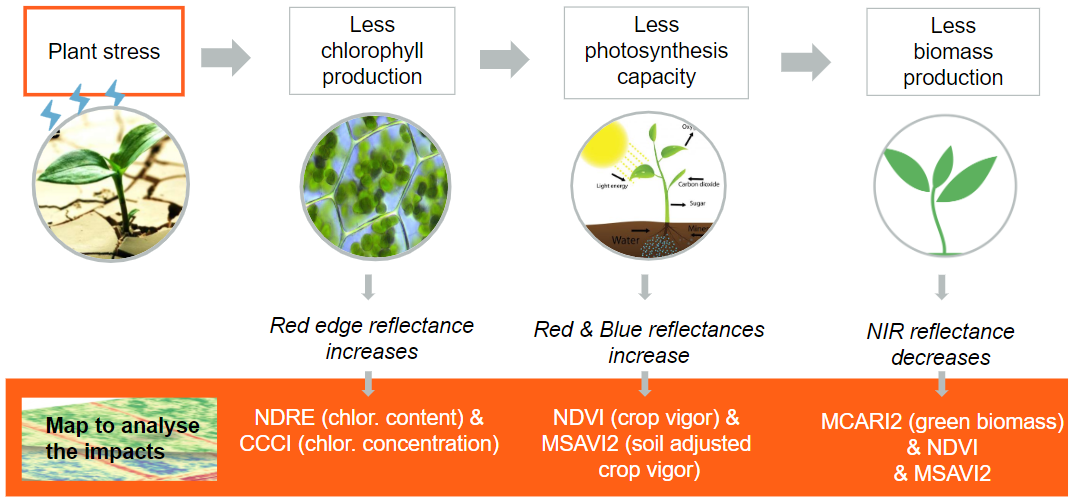
1.3. What is the impact of stress on crops reflectance ?
2. Can you spot individual off-types, e.g. in a seed production field, where genetic purity is crucial ?
For the moment, we do not propose a specific solution to spot individual off-types but they can be detected with different methods, especially if they have a different color, chlorophyll content, vigor, biomass, etc.
3. Would the sensors be able to detect pollen shedding in flowering plants for hybrid crop production ?
We don’t have a solution to detect pollen shedding at the moment. But if the pollen shedding is correlated to a specific and significant plant color that we can detect with the sensor, it would be possible to detect this stage with our software.
4. Can we generate DTM for irrigation systems ?
Yes
5. How can we check the tree counting accuracy ?
We compare the values from the algorithm with the counting from the field (humans walking around the trees and counting them) and the "manual" photo interpretation counting.
Example : for palm trees, ground truth was done with GPS, but no geotagging of each tree (no precision GPS), and two rounds of ground truth was done on each field to assess consistency of ground truth.
Beware that it will only compare two methods results, with their own error (ie : ground truth error and drone error)
6. What is the accuracy of the stand counts ?
The accuracy of stand counts is around 95% with good quality images at the right stage.
7. Can you spot the start of an infection ?
The vegetation indexes we provide based on chlorophyll content/concentration, photosynthetic activity or biomass, allow plant stress detection such as a disease. Then ground sampling is necessary to identify the disease. For the moment we do not provide models to detect specific diseases on a specific crop.
8. Can you determine yield in corn or soybean by plot ?
Aether can provide the plant density and plant height for each plot or microplot (field trial) at different crop stages for a first yield estimation. The accuracy for these indicators is usually around 95%.
9. What size of objects, plants, can we identify ?
We can distinguish an object if its size is 2x to 3x its GSD. That is if GSD = 8cm, we can see objects/plants of 24 cm. According to the crop, we can identify the seedling more or less early.
10. What is the minimum size of a microplot that can be analyzed ?
Today Alteia is working with customers that have different sizes of microplots. There is no minimum size of microplot.
11. Can you detect flowering of cereals and maize ?
For the moment, the flowering analytic only works with Sunflower and Canola, but we work on extending the solution to other crops.